For more than a year, personal freedoms have been curtailed to keep Covid at bay.
That looks likely to change, with ministers proposing to lift many of the remaining restrictions in England on 19 July. The details, set out on Monday, have sparked intense debate.
Prof Neil Ferguson, from Imperial College London, whose modelling led to the first lockdown, has said it is a gamble, but one worth taking.
What is unarguable is that the nature of the pandemic in the UK has changed - and with it so should many of our assumptions.
Covid no longer the deadly virus it was
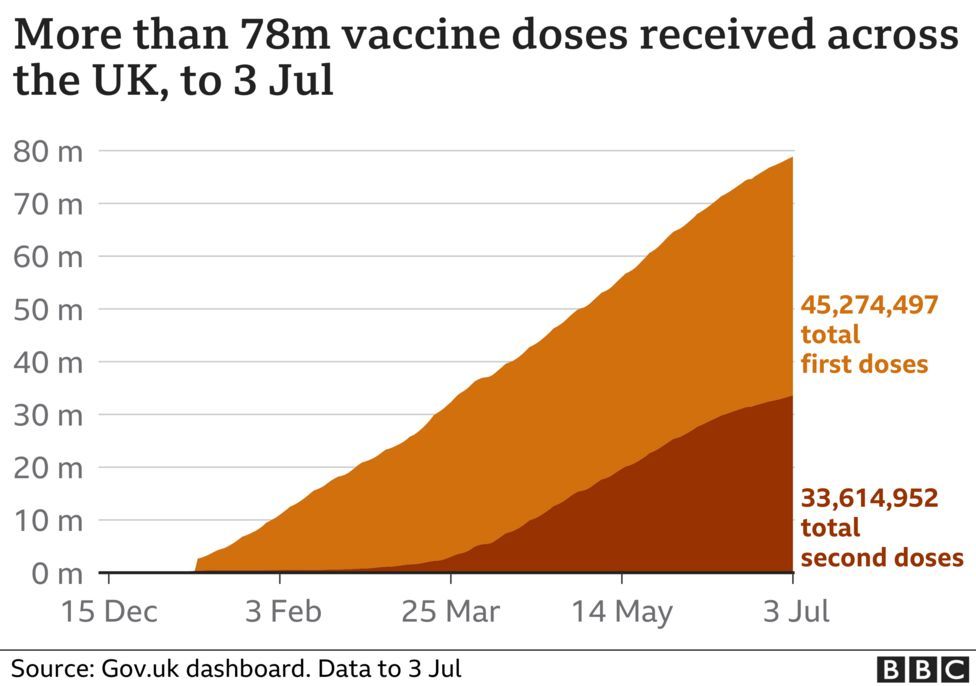
The rollout of the vaccination programme has altered everything, reducing both the individual risk and the wider one to the health system.
Back in January, about one in 10 infections could be expected to translate into a hospital admission 10 days later. Now that figure appears to be somewhere between one in 40 and one in 50.
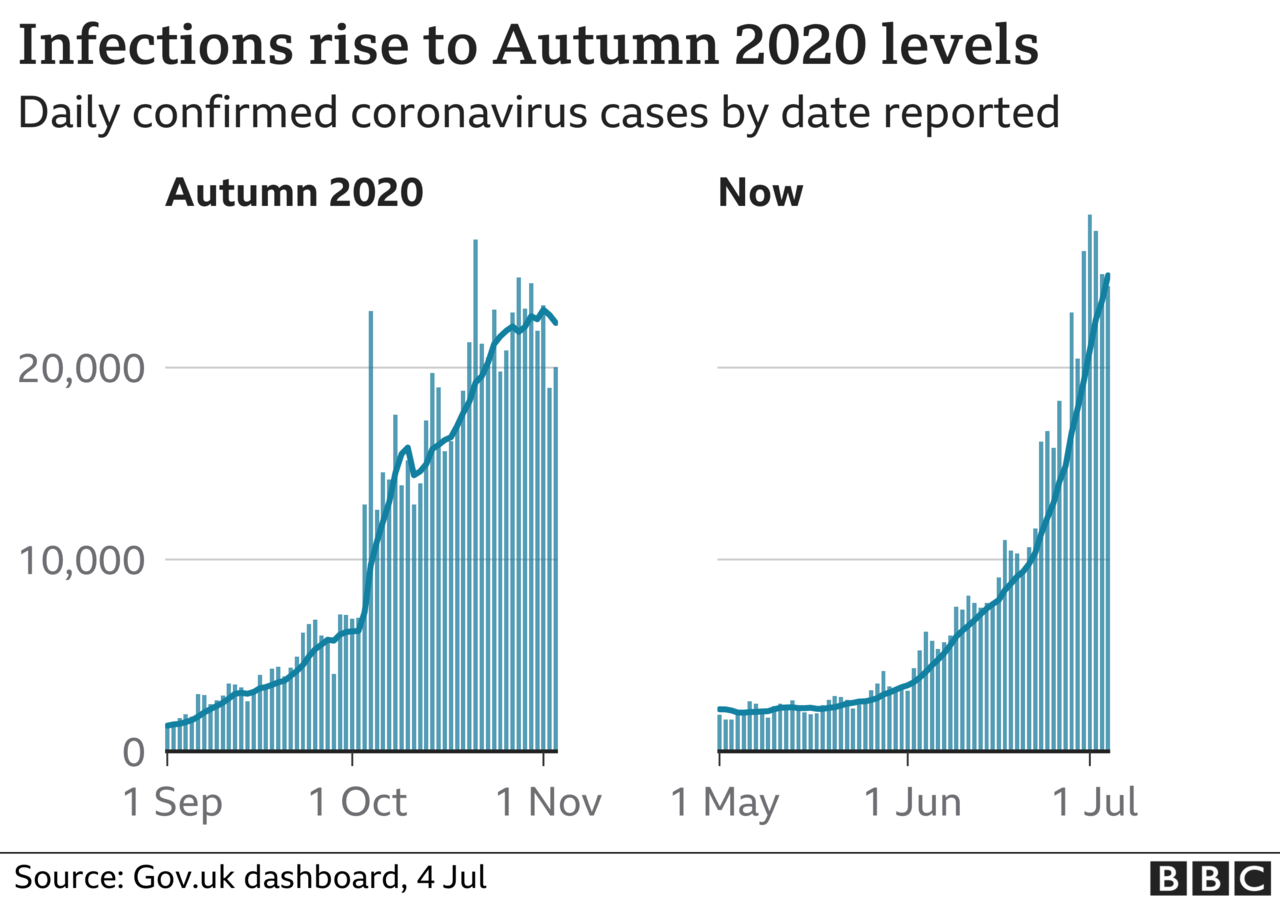
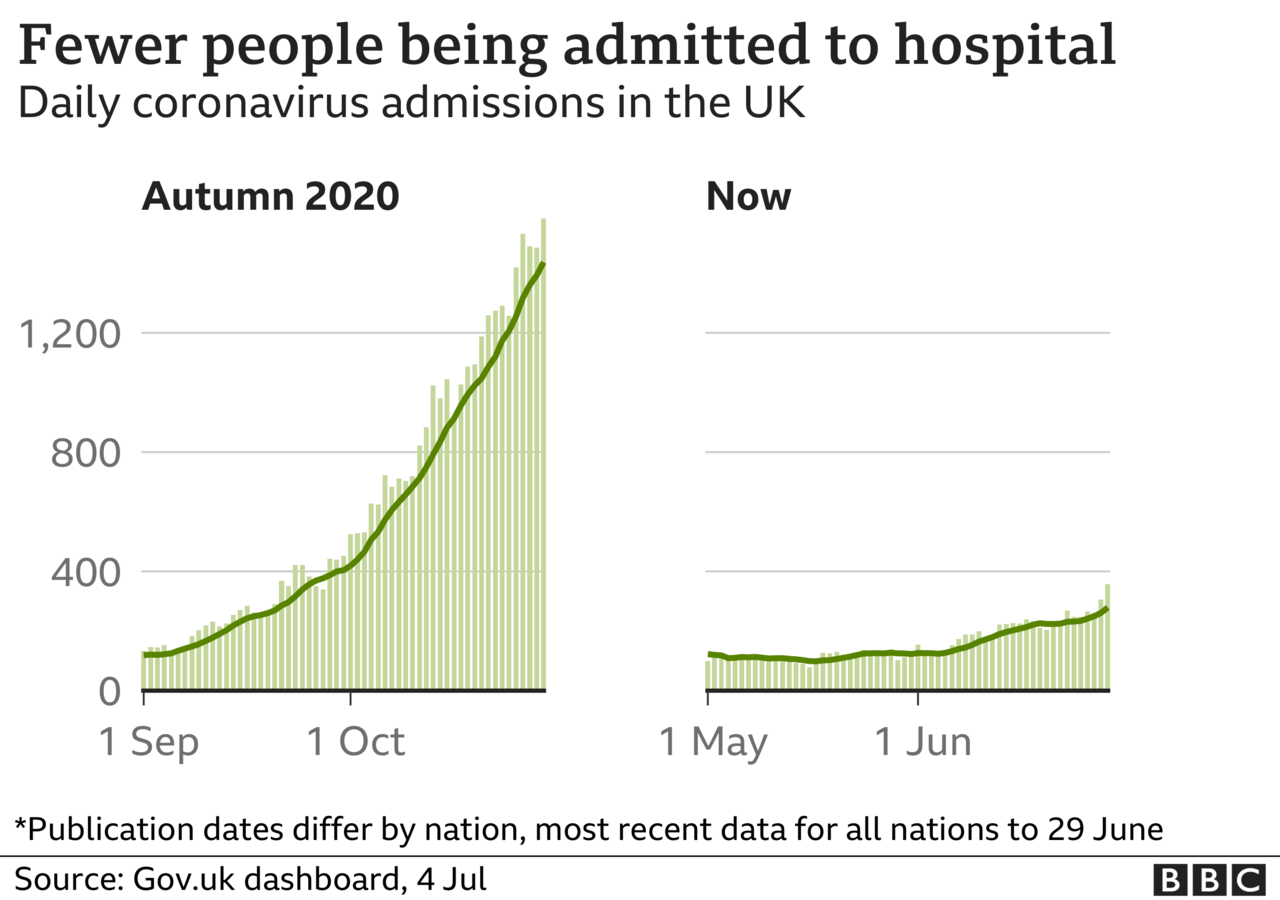
What is more, those ending up in hospital seem to be less sick, and need less intensive treatment.
The risk of death, as a result, has reduced even further. In January about one in 60 cases resulted in someone dying. Today it's fewer than one in 1,000.
Third wave will still be big
But this does not mean England - and the rest of the UK for that matter - is not heading for a significant third wave.
As the charts above show, infection rates are rising. If they rise enough, that has the potential to cause a significant number of hospitalisations, possibly 1,000 a day before summer is out.
Many may wonder how this can happen given how effective the vaccines are.
Individually, those who have had two doses are at a very tiny risk of getting seriously ill, but with infection rates high it means many people are taking that tiny risk at the same time. Add to that those who are unvaccinated or for whom the vaccines do not work as well and you can get a lot of admissions to hospital.
But serious illness happens all the time. In the depths of winter there can be 1,000 admissions a day for respiratory infections.
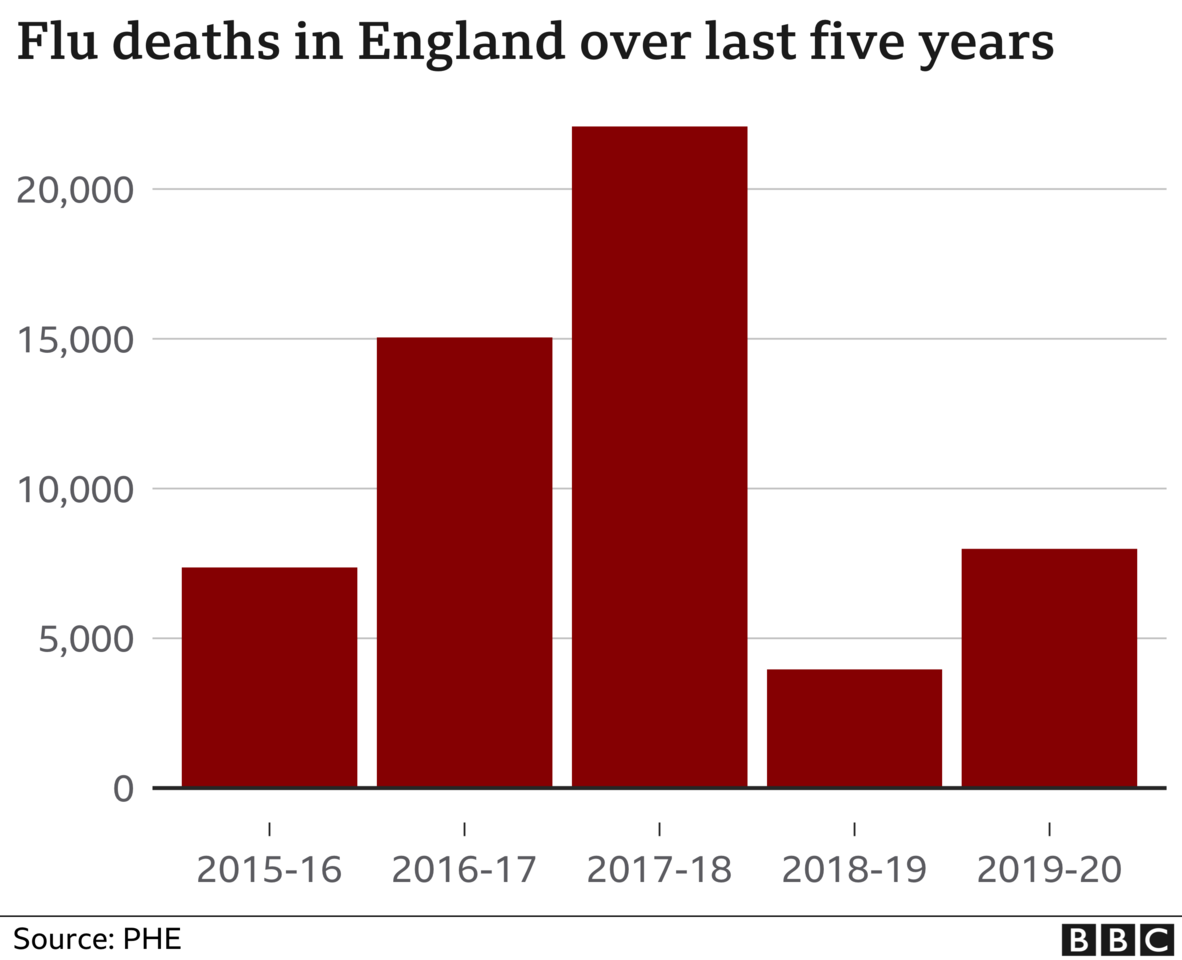
Flu alone killed more than 20,000 people in England in the winter of 2017-18. There was no talk of the need to introduce restrictions or curtail freedoms then.
"That is the context we need to start seeing Covid in," says Prof Robert Dingwall, a sociologist at Nottingham Trent University.
The difficult trade-offs
But why even take the risk? Why not - as scientists on Independent Sage have suggested -wait until the adult vaccination rollout is complete in September?
There was always going to be an "exit wave" once restrictions were lifted. And government scientists are hopeful the wall of immunity built up by natural infection and the vaccine rollout so far will soon kick in and flatten the wave.
The fact remains interventions are not harm-free, so in the end it comes down to difficult judgements about trade-offs.
As the virus presents less of a risk, that in turn shifts the balance on what can be considered proportionate.
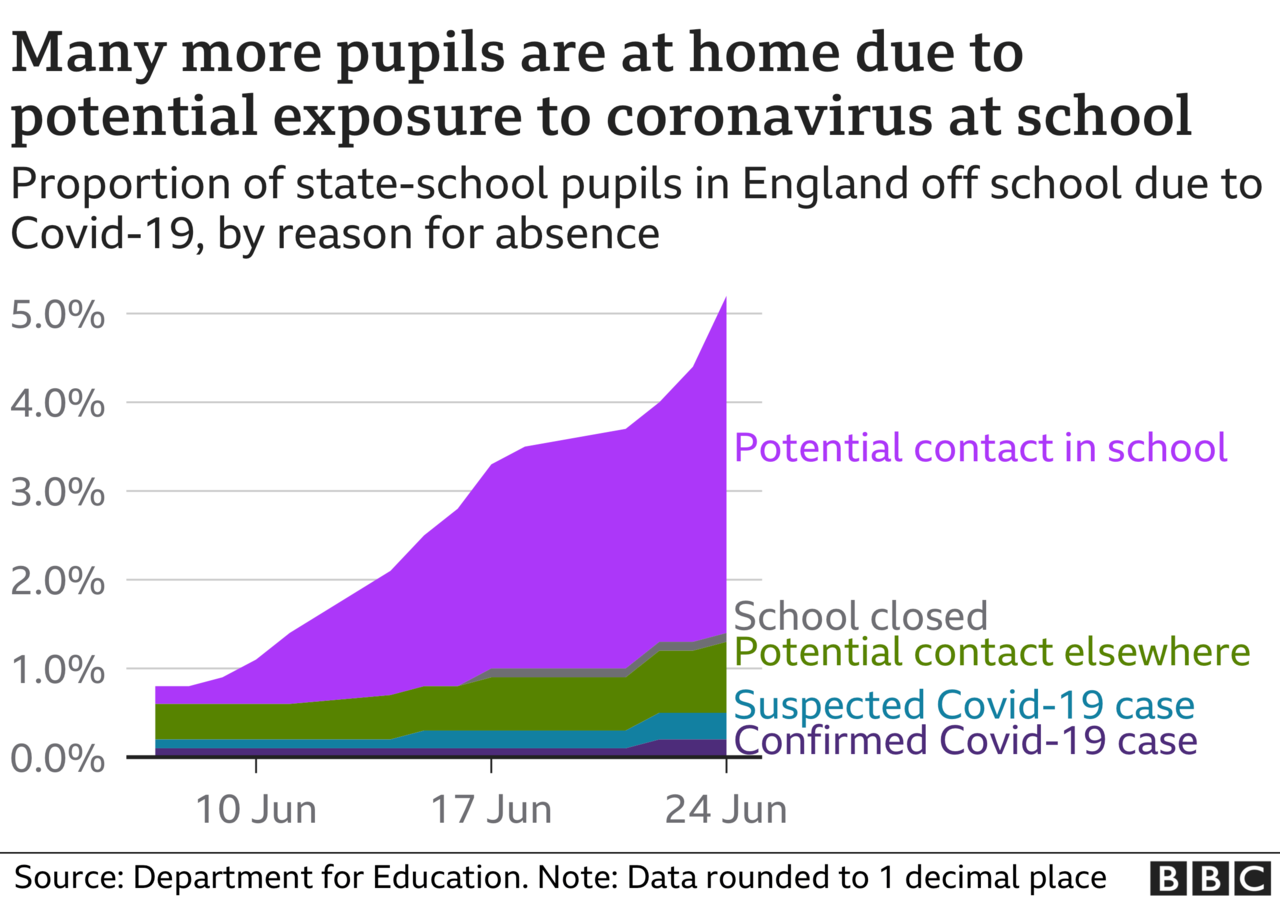
Perhaps the clearest example of this is what is happening with schools where there are currently more than 500,000 children at home self-isolating in England because they were deemed to have close contact with an infected person at school.
That's 20 children out of school for every positive case.
This approach started in September, before vaccines had even completed their clinical trials. The idea was to contain spread of the virus to protect vulnerable adults - children are at incredibly low risk from Covid.
Now that all over-50s have had the chance of a second jab - these are the age groups where 99% of Covid deaths have occurred - the benefits of quarantining children like this is hugely reduced, while the costs in terms of disruption to education are clear to see.
Ministers say they will change this approach in time for September, but should this have been avoided given how much school has been disrupted already?
'Covid will never go away'
There are other arguments for why it should be now.
"Covid will never go away," says Prof Paul Hunter, from the University of East Anglia. "It's inevitable that we're going to catch it repeatedly for the rest of our lives, whether we have had the vaccine or not.
"The issues becomes not whether it is safe to lift all restrictions, but when would it be safest to do so."
Waiting any longer could make the situation worse, he believes, extending the exit wave into the autumn when schools are back and the flu season is getting under way.
It was a view echoed by England's chief medical officer Prof Chris Whitty, who said it had his personal backing when the government unveiled its plans on Monday.
The eyes of the world will be on us
But the idea of letting a virus spread when we have spent so long trying to do the opposite requires a psychological shift.
Dr Muge Cevik, an infectious disease expert at University of St Andrews, says this will take time.
"We need to accept Covid is here. We won't be able to completely stop the spread. We are now at the stage of managing the virus."
She would like to see more emphasis now on recovery, tackling the backlog in hospital care for non-Covid treatments, dealing with the economic fallout and loss of jobs and the emotional and mental health toll the pandemic has had.
But none of this is without risks. What if infection rates keep rising and that wall of immunity is slow to kick in?
Understandable concerns have also been raised about those who are at risk because they have conditions such as blood cancer which mean the vaccines do not work as well or who have a higher chance of exposure because of their jobs, such as shop or factory workers.
There is also Long Covid to contend with - although the risks of this are far from fully understood.
We are, perhaps, the first country to find ourselves in this situation, where we are attempting to return to normal in the face of a rapidly rising rate of infection and a more infectious variant, Delta.
Others will soon face similar dilemmas. It's why the world will be watching what happens on these shores.