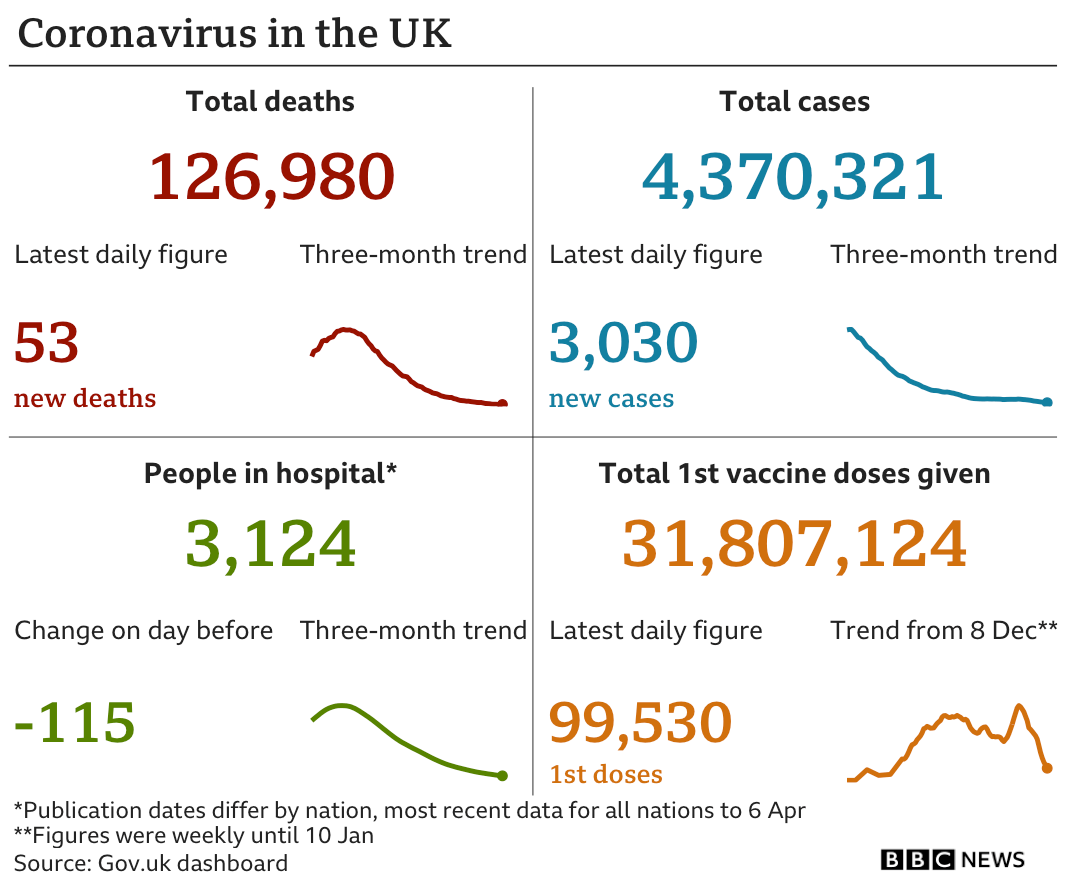
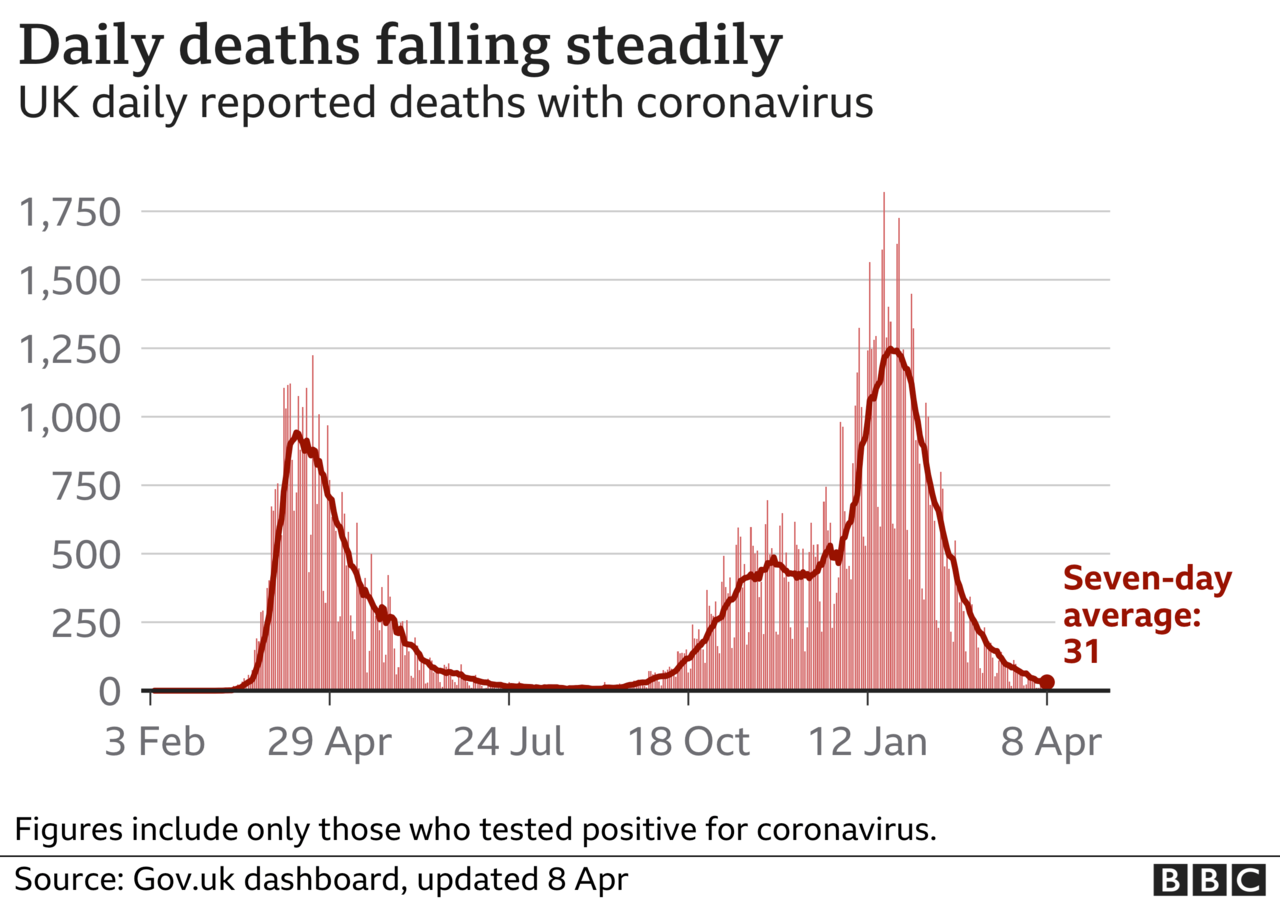
Weekly deaths involving coronavirus in England and Wales have dropped 92% since the peak of the second wave in January, according to official figures.
Meanwhile, the total number of deaths registered in the UK over one week is 5% below the five-year average.
It comes amid continued efforts to reassure the public over the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine's possible link to rare blood clots.
Earlier, Health Secretary Matt Hancock said the jab remained safe.
He urged those who had received one dose to take up their second and said the UK was on track to vaccinate all adults by 31 July.
Figures from the Office of National Statistics showed there were 712 deaths involving Covid in the week ending 19 March, down from 8,945 in late January.
The largest falls were seen among the oldest age groups, with deaths falling 92.9% among those aged 80 and over and 93.4% for the 75 to 79 age group, compared to 83.7% for those aged 60 to 64.
Separate figures showed the number of deaths registered in the UK in the week ending 26 March was 11,439, which was 5% below the five-year average. Last week, deaths were 8% below the 5-year average.
Some 799 of these deaths involved coronavirus.
Adults aged over 80 were the second priority group for vaccination, followed by over-75s and over 70s. The government says everyone in these groups was offered a jab by mid-February.
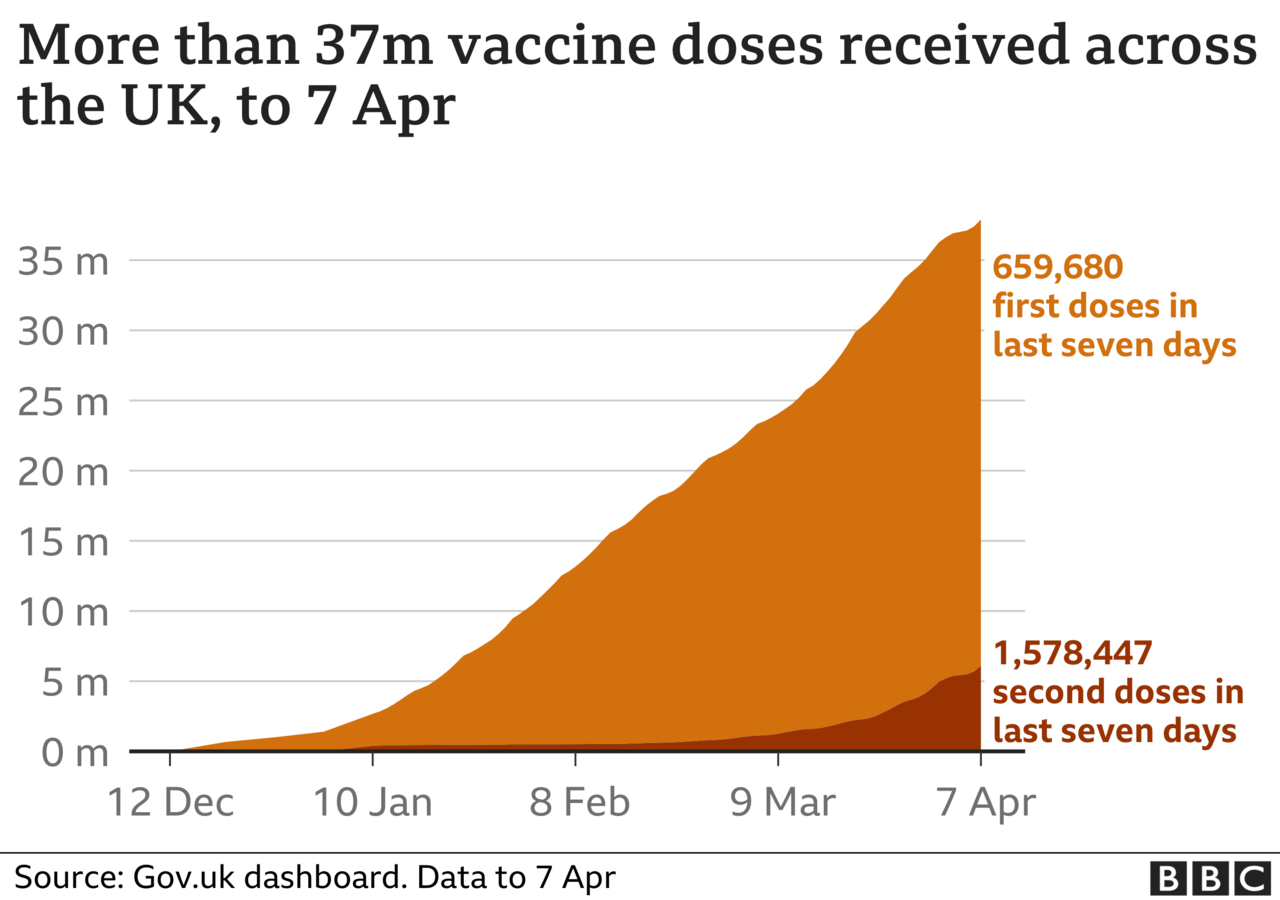
Figures on Thursday showed the UK's vaccination programme had recovered after a lull over Easter, with an extra 408,396 second doses administered and 99,530 first doses. The number of people fully vaccinated is now over six million, while 31.8 million have received just one dose.
Another 3,030 confirmed cases were reported, along with 53 further deaths within 28 days of a positive test.
Seeking to reassure people who have received a first dose of the Oxford-AstraZeneca jab, Mr Hancock said there was "no evidence" of the rare blood clots after the second dose of the vaccine.
The UK changed policy on Wednesday to offer under-30s an alternative to the AstraZeneca vaccine, after weighing the benefits of vaccination compared to a potential very rare risk of blood clots.
There had been 79 incidents of the clots and 19 deaths among the 20 million Oxford-AstraZeneca doses administered, the UK's Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) said. That equates to a one-in-a-million risk of a fatal side effect.
It said there was no proof the vaccine had caused the clots but the link was getting firmer. Both the MHRA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) said the benefits of the jab outweigh the risks, however.
Mr Hancock said people should have confidence in the safety system for vaccines because it was "able to spot this extremely rare event".
The risk was about the same as taking a long-haul flight, he said.
And he said there was "more than enough" doses of vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna due to arrive to offer an alternative to the 8.5 million UK adults under 30 yet to be vaccinated.
The UK has ordered 40 million doses of the Pfizer vaccine and 17 million of the Moderna jab and also has agreements with several other companies for jabs that are still waiting for approval, including 100 million doses from Valneva and 30 million from Janssen.
A government scientific adviser said communication of the benefits and side-effects was "critical" to avoiding a loss of confidence in the vaccines.
Prof Stephen Reicher told BBC Radio 4's World at One that having a Covid jab is "actually one of the safer things you do in the day".
"Something like 30 or 40 people drown in the bath every year, something like 1,000 people die falling down the stairs, something like 200 die from choking on their breakfast, and that's many, many more deaths than we get from these vaccines," he said.