The Covid-19 epidemic in England is growing, scientists tracking it say - with much of it being driven by younger people who are not yet vaccinated.
The analysis, from the React-1 study, looked at the period 20 May to 7 June.
However, tentative signs in the latest daily data suggest growth may be beginning to slow.
The rollout of vaccinations to younger people is key to reducing further spread, researchers from Imperial College London say.
Since last year, the team has been inviting a representative sample of the population to take Covid swab tests. The researchers found:
* of the 108,911 people tested, 135 were positive - a rise from 0.1% to 0.15%
* most cases were among five- to 12-year-olds and 18- to 24-year-olds
* the reproduction (R) number, of people the average infected person would infect, was an estimated 1.44
The analysis also suggests a strengthening link between cases and hospital admissions, which is also reflected in the government's daily coronavirus data.
The number of new infections is rising, with a seven-day average of 8,404 cases. The UK recorded 11,007 cases on Thursday - the highest number since 12,027 were reported on 19 February.
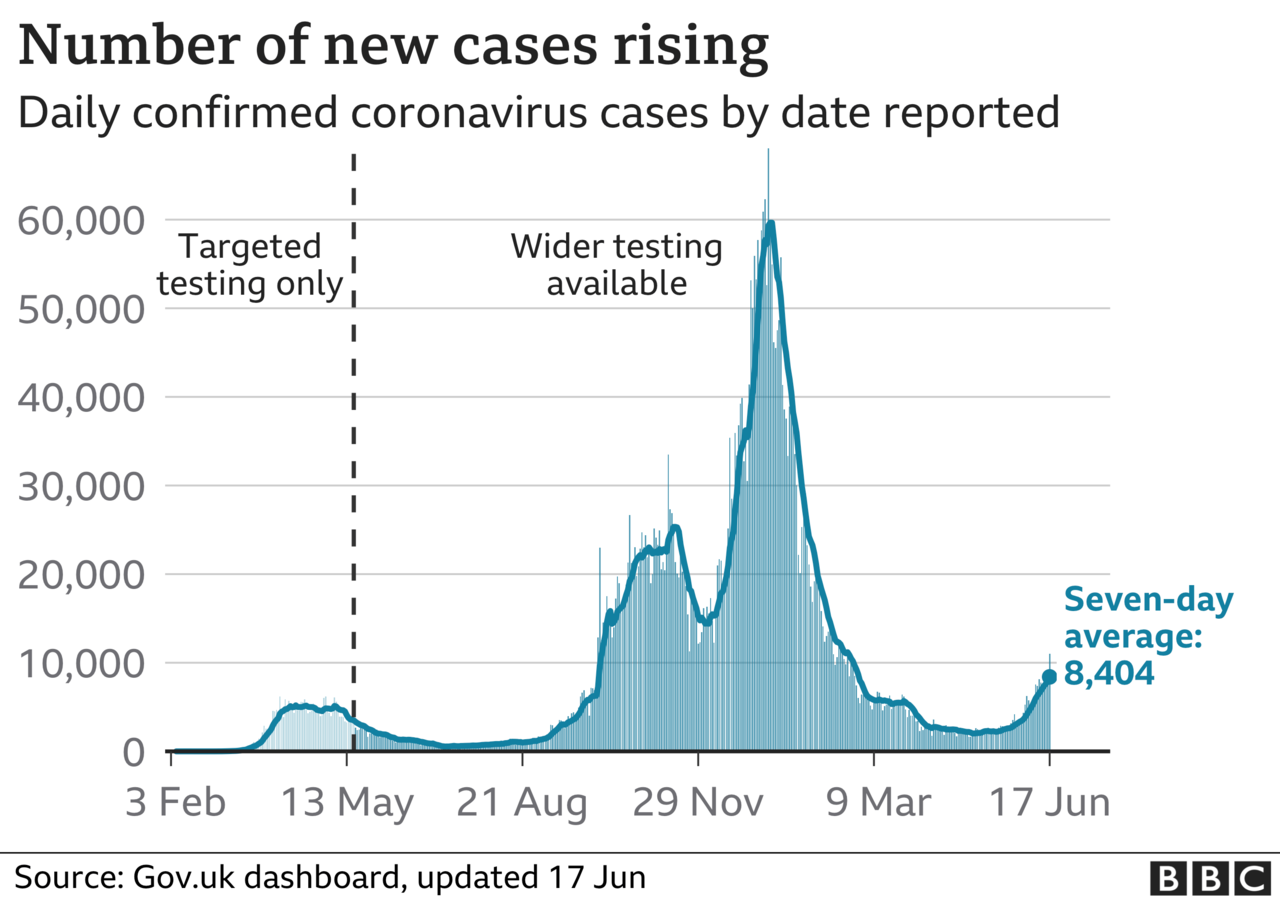
The number of hospitalisations has also increased, with 1,177 patients in hospital as of Monday. However, daily deaths remain low, with a weekly average of nine deaths within 28 days of a positive test.
A further 19 deaths were reported on Thursday.
Prof Paul Elliot, who directs the study, said: "We can take quite a lot of comfort from the fact that when we look in the details, it does appear that there is very, very good protection in the older ages, where there is virtually everyone double vaccinated.
"The government has clearly announced that they want to vaccinate all adults in the period between now and 19 July. That will make a very big difference and increase the total amount of population immunity."
He told BBC News that the study had found the Delta variant first seen in India had overtaken the Alpha (Kent) variant as the UK's dominant strain, and was responsible for an estimated 90% of infections.
England's chief medical officer Prof Chris Whitty said Covid-19 had "not thrown its last surprise at us", warning that he is anticipating case rates will continue to rise over the next few weeks due to the Delta variant being "significantly more transmissible" than the Alpha variant.
He told the NHS Confed Conference he expected a "further winter surge" and said he thought new variants may well lead to booster jabs or revaccination being required over the next two to three years.
Daily data and positive signs?

The picture presented by React is one from 10 days ago. But if we look at the daily figures published by the government, there are some encouraging signs, albeit very tentative.
Last week, cases appeared to be doubling every 10 days, but this week that has slowed to something closer to 14 days.
It still means the epidemic is growing - but it is the first sign of a flattening of cases.
This, of course, could be a false dawn. The rise in infections has largely been driven by north-west England- the top 20 local-authority areas with the highest rates are all in that region.
Infections could easily take off in other areas, speeding up the growth of this wave.
But if this slowing of growth holds, it is very positive.
Government scientists had feared rapid growth right up to 19 July.
This would drive up hospital admissions, albeit, because of the vaccines, at a lower rate than in previous waves.
It is still early days, but data is now a little more encouraging than it was.
Prime Minister Boris Johnson cited the Delta variant's rapid spread when he announced a four-week delay to the lifting of remaining Covid restrictions in England
The government has accelerated its vaccination drive, setting a new target to vaccinate all over-18s with a first dose and two-thirds of adults with a second dose by the same date.
Everyone aged 18 and over in England will be able to book their Covid-19 vaccine from Friday, Health Secretary Matt Hancock announced at the NHS conference.
He said a first dose had now been given to four out of five adults (80.1%).
As of Wednesday more than 30 million people - 58.2% of adults - have had both doses.
New figures published by the Office for National Statistics on Thursday suggest people who test positive for Covid after being vaccinated are less likely to show symptoms and have less of the virus in their body.
The ONS analysis swabbed people at random and picked up asymptomatic infections as well as cases that show up in the daily case numbers.
It showed that the risk of getting infected was highest in the first three weeks after vaccination and fell after a second vaccination. Just under 40% of people who did get infected after vaccination showed symptoms.
There have been about 16,000 suspected cases of coronavirus reinfection detected in England, out of nearly four million cases, according to Public Health England data, although only 53 have been confirmed.















