Tackling inequality at universities must start by tackling disadvantage in society, historian Dame Mary Beard has told the BBC.
The Cambridge professor is stepping down next year after almost 40 years of teaching and research.
A report by the Sutton Trust found the eight top schools had as many Oxbridge acceptances as 2,894 schools and colleges across the UK put together.
Dame Mary said universities could not solve the problems on their own.
"Cambridge and most universities have a problem attracting a widely diverse constituency of students," she told BBC Politics East.
"Cambridge has been extremely active in trying to get students from different backgrounds," said Dame Mary, who is to fund scholarships for two disadvantaged students to study classics at Cambridge as a "retirement present".
"I was an undergraduate at Cambridge when only 12% of the students were women - that was in the 1970s. There has been a revolution in women's opportunities in Cambridge.
"If you want to solve the problem of education inequality you have to do it right from the beginning from the moment the child is born."
Dame Mary, who is also a television presenter, added: "I think a lot of inequalities have widened because of the pandemic. It's been a clear lens on the 'haves' and 'have-nots'."
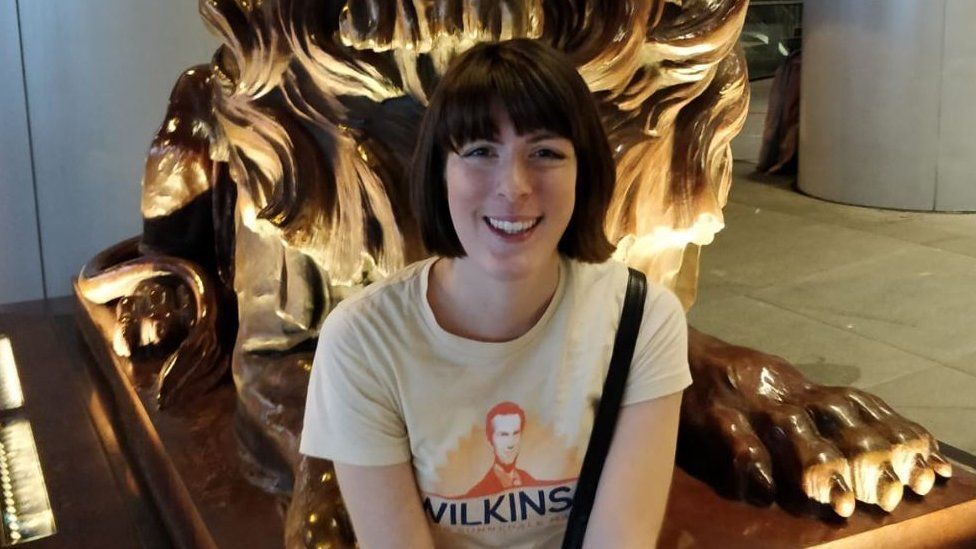

Zoah Hedges-Stocks, from the Leiston area of Suffolk, comes from a family of showmen who have operated fairgrounds for nearly 200 years. She gained a place at Cambridge University in 2009, graduating with a first in history in 2013.
"In my community, it's still not very common to go to university. I thought to myself, if I'm going to do it, I'm going to do it properly and I'll aim for one of the best in the world," she said.
"Growing up on the fair, I was used to speaking to people from all different walks of life, so the thought of going to Cambridge did not intimidate me."
Last year Cambridge University saw 70% of undergraduates come from the state sector (an 8% increase in five years), but that compares to 93% of people in the country going to state schools.
A 2019 report by the National Education Opportunities Network (NEON) found just 2.4% of undergraduates at Cambridge were white students from poorer backgrounds.
But the report found Cambridge was not alone, with the universities of Oxford, Bradford, Bedfordshire, Bristol, Warwick, Surrey, Reading, Aston and Bath having between 2% and 3% from the same demographic.
Prof Graham Virgo, senior pro-vice-chancellor for education at Cambridge, said: "We have been making significant progress, particularly recently, but we know there is more to do.
"This is not an easy area to suddenly say: 'We are going to shift the dial.' And one thing we are really insistent on is we are not going to be reducing standards of entry."
Last month, the BBC reported the University of Cambridge accepted a record number of British students from black, Asian and minority ethnic (BAME) backgrounds (29.3%) in 2020 - up from 27.8% the previous year.
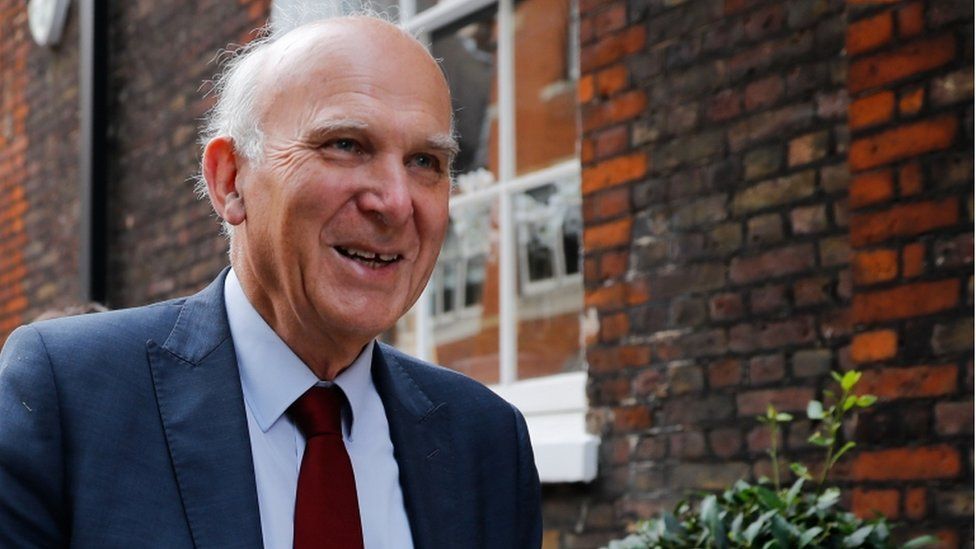

Former Business Secretary and ex-Lib Dem leader Sir Vince Cable said when the coalition government in the 2010s agreed that universities could increase fees, one of the conditions was that "they demonstrate the diversity of their admissions".
He said one way to improve the number of poorer backgrounds going to the top universities, that was looked at by coalition ministers, was using "tests that demonstrate potential rather than attainment".
A Department for Education spokeswoman said: "Most disadvantaged pupils now attend Good or Outstanding schools and, since 2011, disadvantaged pupils had narrowed the gap with their peers at every stage of education up until the pandemic.
"We are targeting investment towards disadvantaged children through our £1.4bn education recovery plans, including £1bn to significantly expand tutoring for young people, so that every child can have the skills and knowledge they need to fulfil their potential."















