In March, the Black employment-population ratio stood higher than for white Americans for the first time since at least 1972.
For the first time since at least 1972, Black Americans are more likely to be employed than their white peers.
That's according to new job market data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The Black employment-population ratio climbed from 59.8% in February to 60.9% in March. The white employment-population ratio climbed from 60.1% in February to 60.2% in March.
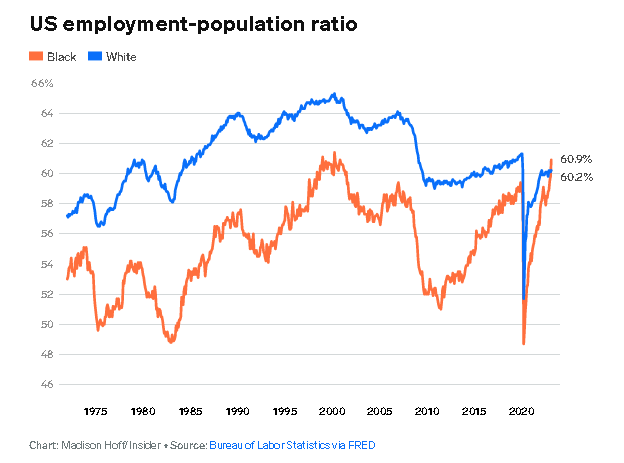
As seen in the above chart the white employment-population ratio has been higher than the Black employment-population ratio in every month since the BLS started measuring both ratios in January 1972, until now. The employment-population ratio measures the share of a group that has a job, meaning that for the first time on record, Black Americans are more likely to currently be working than white Americans.
Additionally, the unemployment rate for Black Americans fell by 0.7 percentage points to 5.0% in March, the lowest rate on record, according to Black unemployment data starting in 1972.
Despite these records, Friday's report did show that the overall US labor market has been slowing down from its recent rapid growth. The US added 236,000 nonfarm payrolls in March, just shy of the median forecast of 239,000 from economists. It was also below February's gains, which was 326,000, according to a recent revision noted in Friday's report, as well as January's revised job gain of 472,000.
That report was still good news for the economy overall, according to Daniel Zhao, lead economist at Glassdoor.
"This report is a Goldilocks report," he told Insider. "It was really great to see that job gains remain strong, and the labor market is resilient, but we're also seeing evidence that things are cooling off gradually."
Zhao added, "and then on top of that, we hit some major milestones, with the Black unemployment rate falling to the lowest level on record."
Black unemployment is still higher than for white Americans, but inequality is shrinking
Black Americans have historically faced obstacles when it comes to employment in the US.
And despite the Black unemployment rate tumbling to a new low, Heidi Shierholz, president of the non-partisan Economic Policy Institute and former chief economist of the US Department of Labor, said on Twitter to "make no mistake" that the rate "is still too high."
"Due to the impact of structural racism on the labor market," she wrote, Black workers as well as Hispanic workers "have much higher" rates than for white workers. "But the strength of this recovery has led to progress on reducing racial employment gaps," she wrote.
Which is what makes March's low unemployment rate for Black Americans, and a higher employment-population ratio than the white employment-population ratio, so novel.
"The reduced racial inequities in the labor market are wonderful to see and that's one of the byproducts of a tight labor market, in that when there's more competition for workers, folks who have been traditionally more disadvantaged, more marginalized, see more job opportunities," Nick Bunker, economic research director for North America at Indeed Hiring Lab, told Insider.
"That's a very encouraging consequence of this tight labor market that we're seeing right now — is that while certainly not all of them, but some of the racial inequities we've seen in our economy are dissipating," Bunker added.
And although Zhao viewed the report positively overall, he cautioned that people should keep the "age structure of the population" in mind when looking at the employment-population ratios.
"If you're not adjusting for age and looking at the prime-age ratio, what you can have happen is if the white population is aging faster than the Black population, the white employment-population ratio will actually fall faster than the Black employment-population ratio," he said.
He added that overall, the numbers are a promising sign for Black Americans.
"A hot labor market can lift all boats," Zhao said. "It incentivizes employers to reach out to pools of talent they've historically overlooked. Whether that means reaching out to them specifically or taking other actions that might disproportionately help underrepresented groups."















